For many online retailers, improving website speed and performance has been an afterthought—a bonus to creating a great site rather than an integral part of what makes the site great.
You may be thinking that building a great and functional website is headache enough. And now there is maintenance to think about.
Indeed, too often, if a website is not maintained well and neglected, it can lead to poor performance and may incur revenue loss for your business.
If you identify with what you’re currently facing, that is, slow site speed and lower than optimal performance, it isn’t too late to rectify the poor website performance that website negligence brings.
This article highlights the top 6 reasons for poor website performance and how to rectify each issue.
Here are the reasons and how to fix them.
1. No Caching Layer
Caching is probably the most important technique for speed improvement on the web. Caching is a technique where the storage of a copy of your website files is in a place called a web cache.
Without caching, the client must request your website’s assets from your origin server every time instead of using a local cache. The lack of caching layers might lead to slower response times as the server limits the number of requests it can handle. Load times go up after every request goes into a queue.
How to Fix Caching Issues
Use Caching Plugin
If you are using content management software (CMS) like WordPress, you can use caching plugins like “WP Super Cache” or “W3 Total Cache“. They are free and they offer good caching capacity.
Setup Server Caching Rules
You can set up caching rules on your website. You can change them through your server.
Most web hosting companies would have server caching rules enabled but it will be good to check with your web host to see if they have caching enabled for your website.
Use a content delivery network (CDN)
A content delivery network (CDN) is a collection of geographically distributed web servers that store static or dynamic content for fast delivery to end users.
A CDN is usually used with web hosting. The goal is to make it easier to serve pages from a nearby server to improve your website’s performance.
There are many CDN service providers, and a number of them offer their basic services for free. Some recommended CSN service providers include Cloudflare, StackPath, or Amazon CloudFront.
2. Heavy Website Code
When a website’s code is poorly written, which can cause the website to be “heavy” in code.
The website can also be “heavy” when too many plugins are installed. Plugins can be a culprit for stacking repeated codes and bloating the size of the website.
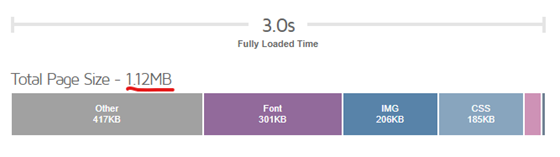
In general, 1MB+ is the ideal website page if we want a fast-loading page. You can easily check your website size by visiting GTMetrix:
How to Fix Poorly Written Code
Code Minification
Minifying JavaScript and CSS files and then combining them into single bundles. Minifying the code can be a challenge as it involves coding. The good news is that caching plugins (mentioned above) has code modification feature built into their software.
Reduce the Number of Plugins Used
You should review the use of plugins and remove plugins deemed redundant. Always test the website when you remove a plugin to ensure that the plugin does not remove the features without an alternative.
3. Unoptimized Images

Graphics are used on many websites.
They will slow down your website if your images are not compressed or you use too high a resolution.
When your website is slow, it will make your visitors wait. If this happens, your visitors will leave the page quickly, and they may forget about your company and your products.
How to Fix Unoptimized Images
Compress Your Images
To ensure that your graphics load quickly and smoothly, you must compress your images using an image compressor.
You can use online software like TinyPNG.com to compress your images easily.
Lazy Loading Your Images
Lazy loading refers to loading the images that users are currently looking at and are the only images that can be loaded. If the user doesn’t scroll to the image, it won’t load.
Use Next Generation Image Formats
The next generation of image formats like WebP and JPEG XR has better compression and quality characteristics. If you use them, you can reduce file size without compromising on quality.
4. Too Many HTTP Requests
Each image, Javascript file, and CSS file are considered an HTTP request. So it’s clear that too many files can lead to many HTTP requests.
When a user visits your web page, the browser performs several requests to load each file, so it’s better to have lower HTTP requests.
In general, we should aim for less than 50 requests.
How to Fix Too Many HTTP Requests
The easiest way to reduce HTTP requests is to reduce the number of files or consider combining multiple files into one. Combining files can easily reduce the number of HTTP requests.
5. Too Many External Scripts
Too many external scripts can increase loading time as there is a need to wait for the script from another server. Some culprits of external scripts would include embedding YouTube videos, Google Analytics code, fonts, and advertisement scripts.
The above scripts can be great assets for enhancing a web page, but there is a need to balance external scripts with website performance.
How to Fix External Scripts
Lazy Loading External Scripts
Similar to images, you can lazy load external scripts when the user scrolls to the section.
Place External Script at the Bottom of the Page
A webpage is loaded in the sequence of the lines of code, so it makes sense to place the external script at the bottom of the page, so they are last loaded.
Load External Script Asynchronously
Asynchronous loading means a script is loaded in parallel with other scripts, increasing the website’s speed. The good news is that Google Analytics is loaded as an asynchronous script.
6. Bad Hosting
Your web hosting service provider greatly affects how fast your website loads.
If you have tried resolving based on all the above points, you should consider switching your hosting provider.
The problem is that most websites choose to host on shared web servers. These servers might have too many users or be unable to upgrade their servers fast enough. They could even be having issues with their hardware.
How to Fix Bad Hosting

As you can see, shared hosting can cause website performance as it will depend on the activities of other users.
Where possible, always look for a virtual private server or cloud hosting offered by companies like WebAble.Host.
WebAble.Host is a serverless hosting platform for hosting your website. It is easy to use, and you would need lesser support. It offers reliability, performance, security, and scalability for your websites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several reasons why websites tend to perform poorly.
The most common reason is that the website owner hasn’t done their due diligence in creating a website that performs well.
The top 6 reasons are not exhaustive but sufficient to enable you to have a better-performing website.
Do you have any other ideas for fixing a slow website? Do share with us.
Websparks is a digital and full-web solutions company based in Singapore. We are an award-winning company that specialises in various digital solutions to bring the best to our clients.
Check out our portfolio and services.
Contact us if you would like to develop or improve your website.